Events Walkthrough
This walkthrough covers how to build with Dropbox Sign Events and Callbacks (aka "webhooks), which are payloads of event metadata automatically sent to your app when something happens in Dropbox Sign.
This resource centers implementation details, examples, and building with webhooks. For a higher-level overview of Dropbox Sign Events, please refer to the Events Overview section of the documentation.
Event Scoping
When using the Dropbox Sign API, events can occur in two contexts: at the Account level and at the App level. Events that are scoped to an Account are called Account Callbacks while events scoped to an App are called App Callbacks. We recommend referring to their respective pages for more detailed information.
Account Callbacks
Account Callbacks notify your app when an event happens involving your account by sending the event payload to your account callback url. The account callback url can be configured on the Dropbox Sign website or by calling the Dropbox Sign API. You can see examples of both in the Set Account Callback Url section of this walkthrough.
App Callbacks
App Callbacks are triggered when an event happens that is associated with a specific app. When these events occur, Dropbox Sign sends the event to the app callback url. Your Dropbox Sign account can have multiple API apps that each have their own app callback url. When an event is triggered by an API request that includes aclient_id, the event payload is sent to that specific app's callback url.
You can change an app callback url through the Dropbox Sign website or Dropbox Sign API. There are examples of both in the Set App Callback Url section of this walkthrough.Setting Up Dropbox Sign Events
Enabling Dropbox Sign Events (webhooks) requires two distinct steps:
- Setting the callback url at the account or app level, which are both covered in the sections directly below.
- Responding to the event to verify it was received.
warning
In order to help protect sensitive data passed through your callback events, we will require callback URLs to use HTTPS starting November 30, 2024. Please use the sections below to update your account and app callback URLs. Any callback URL not using HTTPS on December 1, 2024, will stop receiving Sign callback events.
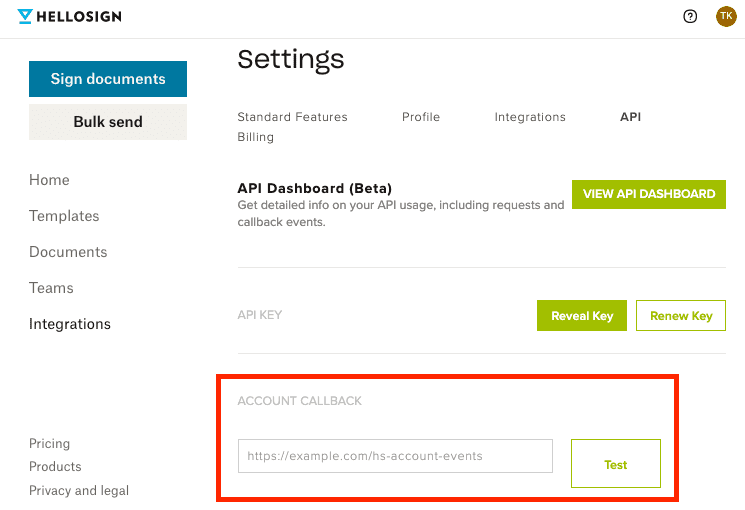
Set Account Callback Url
- You can change your account callback url with the Dropbox Sign API by sending a PUT request to /account and passing a
callback_url.curl -X POST 'https://api.hellosign.com/v3/account' \ -u 'YOUR_API_KEY:' \ -F 'callback_url=https://example.com/hs-account-events' - Alternatively, your account callback url can be changed from your API settings page.
Set App Callback Url
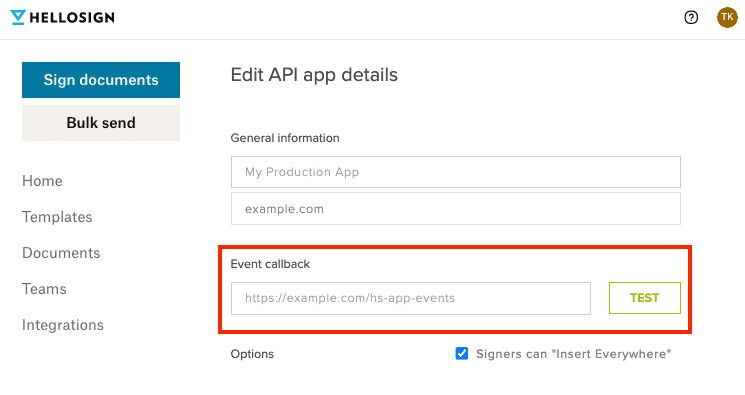
- Your app callback url can be changed by sending a
callback_urlparameter in a PUT request to /api_app/{client_id}.curl -X POST 'https://api.hellosign.com/v3/api_app/0dd3b823a682527788c4e40cb7b6f7e9' \ -u 'YOUR_API_KEY:' \ -F 'name=Your Awesome App' \ -F 'callback_url=https://example.com/hs-app-events' - In the Dropbox Sign web app, you can change your app callback url from the API app's setting page, which you can navigate to from the API settings page.
Responding to Events
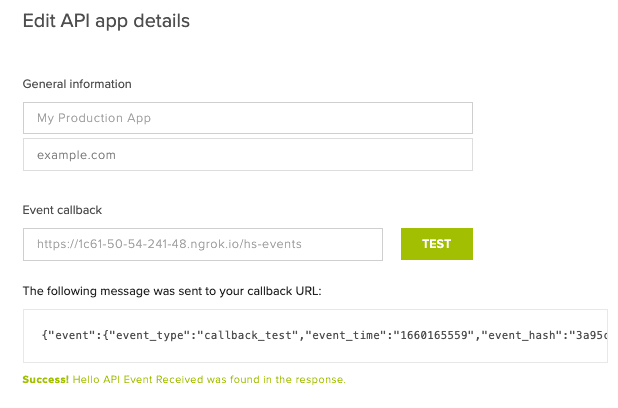
Dropbox Sign sends events to a callback url and expects a specific response in order to verify that events are being sent to a live server. Once an event is sent, the callback url must return an HTTP200 with a response body that contains the string Hello API Event Received. If no response is received, Dropbox Sign considers that a failed callback and the event will be sent again later.Failed Callbacks
Too many consecutive failed callbacks will result in Dropbox Sign deactivating webhooks for a callback url. Once deactivated, Dropbox Sign will stop sending events until a new callback url is added. Read more about this behavior in the Failures and Retries section.
Here's a basic example in Nodejs:
// This sample is stripped down
// Use for reference only
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.post('/hs-events', (req, res) => {
res.set('content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.status(200).send('Hello API Event Received');
});Testing your Callback Url
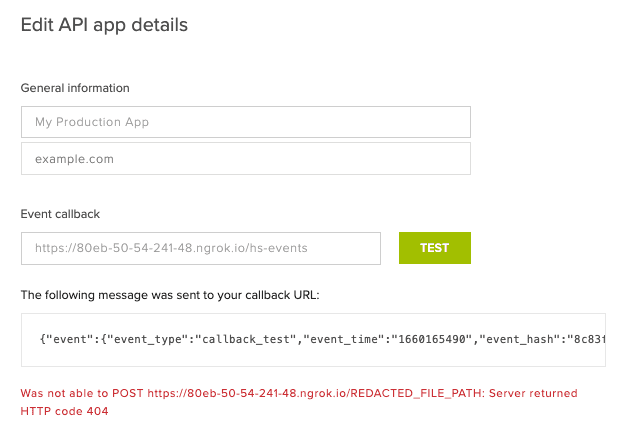
When setting the callback url for your app or account in the Dropbox Sign web UI, you can trigger a test event by clicking the test button next to the field. This is a great way to verify that your webhook handler is responding to events successfully.
Callback Request Format
Once you've setup a callback url, Dropbox Sign sends event data to that URL in the form of POST requests. This section contains information about how those requests are formatted so you can better understand how to interact with the event data.
Content Type
By default, the POST requests are sent asmultipart/form-data with the event details in a field named json.All of our current SDKs include an Event Callback Helper to facilitate parsing event data.
Event Payload
Event payloads always include anevent field, which contains basic information about the event that occurred (such as time and type). Event payloads may include an account, signature_request, or template depending on what event took place.Here's an example of an event payload for a signature_request_sent event:nullEvent Type
Every event payload contains anevent_type parameter that provides the name of the specific event that occurred:{
"event": {
"event_time": "1348177752",
"event_type": "signature_request_sent",
"event_hash": "3a31324d1919d7cdc849ff407adf38fc01e01107d9400b028ff8c892469ca947",
"event_metadata": {
"related_signature_id": "ad4d8a769b555fa5ef38691465d426682bf2c992",
"reported_for_account_id": "63522885f9261e2b04eea043933ee7313eb674fd",
"reported_for_app_id": null
}
},
"signature_request": {
...
}
}event_type is the best approach to filtering for specific events and automating your integration with the Dropbox Sign API. For example, we recommend using signature_request_all_signed as the best indicator that a signature request has been fully completed and can be downloaded using /signature_request/file:if (event.event_type === "signature_request_all_signed") {
// download completed signature request
}You can see a complete list of possible events in the Event Names section of the overview page. This list will be updated as new events are added.
Securing your Callback Handler
Make sure that webhook events are originating from Dropbox Sign by using the following recommended methods.
IP Address Whitelisting
We have made a JSON file containing the full list of IP addresses that webhook events may come from available for download.
Note: This list will be automatically updated if the IP addresses change. We recommend checking this list periodically to ensure your callback handler is secure.
HTTP Headers
We provide a couple of headers on callback requests to help you identify them.
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| User-Agent | A token identifying us | Dropbox Sign API |
| Content-Sha256 | A base64 encoded SHA256 signature of the request's JSON payload, generated using your API key. echo -n $json | openssl dgst -sha256 -hmac $apiKey | Example value: Y2Y2MzVhOTdiZDVhZmVhNWRiYWJmMmRiZGRhOGQzYWE3OGU1NWIxNDkzMzgzNzdjMWI5M2Y1OGEzYzEyNzZjMg= |
Event Hash Verification
Every event payload contains anevent_hash that can be used to verify the event is coming from Dropbox Sign. By generating your own hash and comparing that against the one sent with the Dropbox Sign event, you can ensure you're only processing events that you know were sent by Dropbox Sign. The mechanism being used here is called HMAC, which stands for "hash-based message authentication code". To generate your own hash, you'll need to use your API key (on your API settings page) as well as the
event_type and event_time from the event payload: echo -n $event_time$event_type | openssl dgst -sha256 -hmac $apikeySDK Event Callback Helper
Our current SDKs have helper methods which can help verify callbacks came from Dropbox Sign.
Below are examples on how to implement these for each of our official SDKs:
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . "/vendor/autoload.php";
// use your API key
$api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY";
// $callback_data represents data we send to you
$callback_data = json_decode($_POST["json"] ?? [], true);
$callback_event = Dropbox\Sign\Model\EventCallbackRequest::init($callback_data);
// verify that a callback came from HelloSign.com
if (Dropbox\Sign\EventCallbackHelper::isValid($api_key, $callback_event)) {
// one of "account_callback" or "api_app_callback"
$callback_type = Dropbox\Sign\EventCallbackHelper::getCallbackType($callback_event);
// do your magic below!
}import com.dropbox.sign.EventCallbackHelper;
import com.dropbox.sign.model.EventCallbackRequest;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// use your API key
var apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY";
// callbackData represents data we send to you
var callbackData = request.getParameter("json");
var callbackEvent = EventCallbackRequest.init(callbackData);
// verify that a callback came from HelloSign.com
if (EventCallbackHelper.isValid(apiKey, callbackEvent)) {
// one of "account_callback" or "api_app_callback"
var callbackType = EventCallbackHelper.getCallbackType(callbackEvent);
// do your magic below!
}
}
}from dropbox_sign import EventCallbackHelper
from dropbox_sign.models import EventCallbackRequest
import json
# use your API key
api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY"
# callback_data represents data we send to you
callback_data = json.loads(request.POST.get('json', ''))
callback_event = EventCallbackRequest.init(callback_data)
# verify that a callback came from HelloSign.com
if EventCallbackHelper.is_valid(api_key, callback_event):
# one of "account_callback" or "api_app_callback"
callback_type = EventCallbackHelper.get_callback_type(callback_event)
# do your magic below!require "dropbox-sign"
# use your API key
api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY"
# callback_data represents data we send to you
callback_data = JSON.parse(req.POST.json, :symbolize_names => true)
callback_event = Dropbox::Sign::EventCallbackRequest.init(callback_data)
# verify that a callback came from HelloSign.com
if Dropbox::Sign::EventCallbackHelper.is_valid(api_key, callback_event)
# one of "account_callback" or "api_app_callback"
callback_type = Dropbox::Sign::EventCallbackHelper.get_callback_type(callback_event)
# do your magic below!
endimport { EventCallbackRequest, EventCallbackHelper } from "@dropbox/sign";
// use your API key
const api_key = 'YOUR_API_KEY';
// callback_data represents data we send to you
const callback_data = JSON.parse(req.body.json);
const callback_event = EventCallbackRequest.init(callback_data);
// verify that a callback came from HelloSign.com
if (EventCallbackHelper.isValid(api_key, callback_event)) {
// one of "account_callback" or "api_app_callback"
const callback_type = EventCallbackHelper.getCallbackType(callback_event);
// do your magic below!
}using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Dropbox.Sign.Model;
using Dropbox.Sign;
public class Example
{
public static void Main()
{
// use your API key
var apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY";
// callbackData represents data we send to you
var callbackData = Request.Form["json"];;
var callbackEvent = EventCallbackRequest.Init(callbackData);
// verify that a callback came from HelloSign.com
if (EventCallbackHelper.IsValid(apiKey, callbackEvent))
{
// one of "account_callback" or "api_app_callback"
var callbackType = EventCallbackHelper.GetCallbackType(callbackEvent);
// do your magic below!
}
}
}Failures and Retries
If your callback url is not reachable or returns a non-successful response, we will retry POSTing the event up to 6 times, with each retry interval being longer than the previous one. If the sixth retry fails, you will begin receiving notifications by email.
After 10 consecutive failures, your callback URL will be automatically cleared.
Please note that our requests will timeout after 30 seconds, so callbacks will fail if your server takes longer than that to respond. The retry pattern is described below.
| Retry | Delay After Previous Attempt |
|---|---|
| First | 5 minutes |
| Second | 15 minutes |
| Third | 45 minutes |
| Fourth | 2 hours 15 minutes |
| Fifth | 6 hours 45 minutes |
| Sixth | 20 hours 15 minutes |
The above retry pattern may not always be exact, but it is a good approximation of the retry pattern we use.